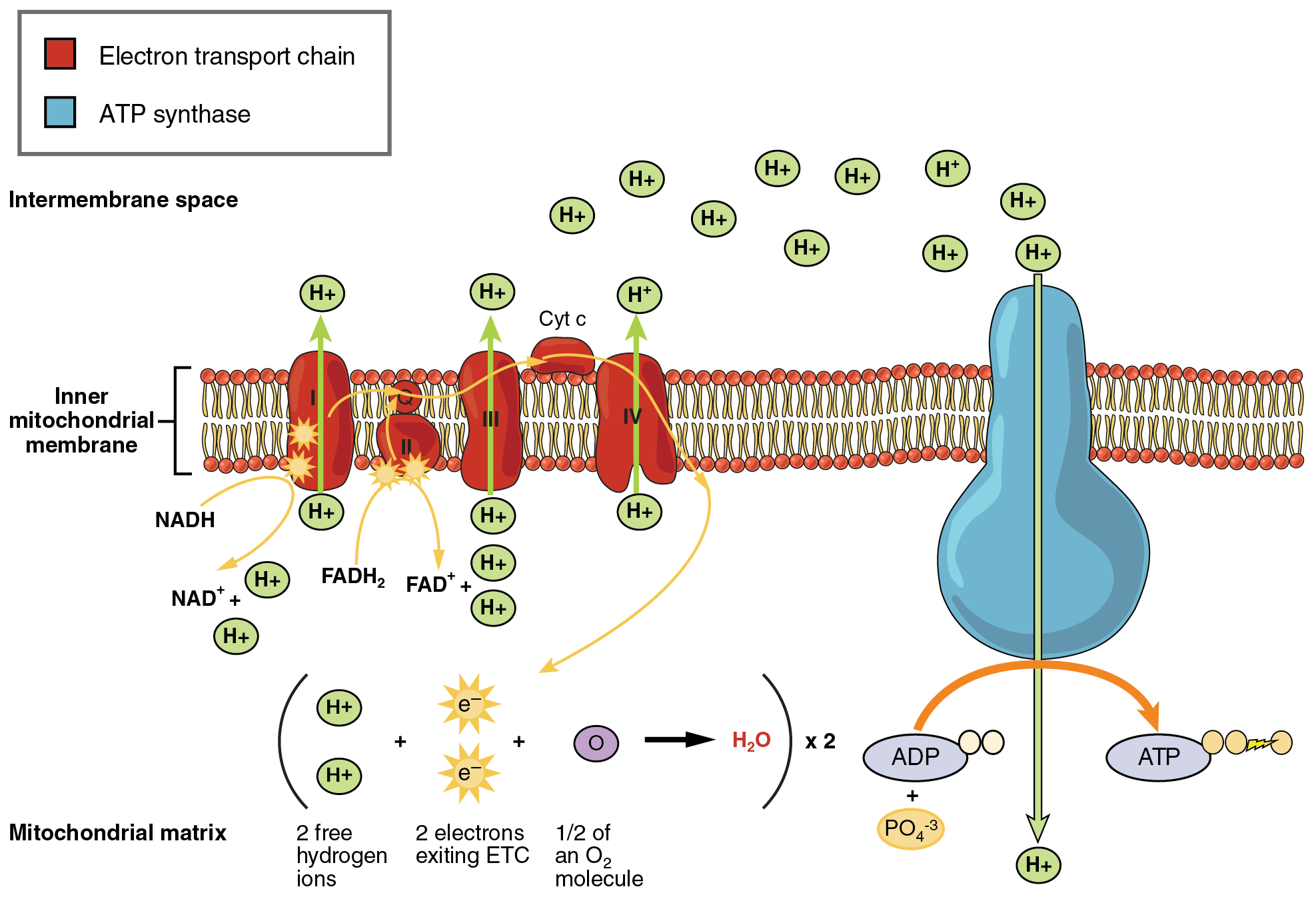
This step also produces more atp.
You will also investigate the effects of temperature, light, or seed type on the rate of respiration. The 10 steps of glycolysis are organized by the order in which specific enzymes act upon the system. The two basic requirements for cellular respiration is glucose and oxygen. Insert the table into a word document and provide a discussion of how each sub part. cellular respiration (aerobic respiration) (2 points) b.

In order to move from glycolysis to the citric acid cycle, pyruvate molecules (the output of glycolysis) must be oxidized in a.
There are three steps of cellular respiration and they always occur in this order: Learn about cellular respiration and how the electron transport chain uses the products of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle to complete the final steps in the process and convert food into energy. During cellular respiration, the energy from glucose is released in the presence of oxygen. Glycolysis, the kreb's cycles, and the electron transport chain, all which go through a series of redox reactions. This chapter will teach you the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration and take you. This step also produces more atp. The general chemical formula for cellular respiration is glucose. Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen, while anaerobic metabolism occurs in the absence of oxygen. Briefly describe each step, where each occurs in a eukaryotic cell. cellular respiration is a collection of three unique metabolic pathways: cellular respiration is a catabolic process, resulting in the oxidation of organic molecules to release energy. What is the order of macromolecules you would use for energy. There are three main stages of cellular respiration:
It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. The most important factor to remember during this process is that these steps have to occur in order, or in other words; We acquire glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6) from the food we eat. Glycolysis (cellular respiration 1 st stage) "the breakdown of glucose up to the formation of pyruvic acid is called glycolysis." Two phosphate groups are attached to one molecule of glucose, atp converted to adp.

Briefly describe each step, where each occurs in a eukaryotic cell.
And i'm going to introduce them to you right now, This chapter will teach you the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration and take you. Where do each part of cellular respiration occur? There are three steps of cellular respiration and they always occur in this order: This week we covered the details of cellular respiration. cellular respiration takes place in various steps. Home — essay samples — science — cellular respiration — analysis of the four steps of cellular respiration this essay has been submitted by a student. Glycolysis is the first step in cellular respiration where the glucose molecule is catabolized to form pyruvate through a series of 10 steps. Glycolysis (cellular respiration 1 st stage) "the breakdown of glucose up to the formation of pyruvic acid is called glycolysis." Your assignment this week is in two parts. cellular respiration gives both plant and animal cells the useable energy, aka atp, that they need to do stuff. But there's a huge variation here and people are really still studying this idea. Correspondingly, what are the steps of cellular respiration in order?
cellular respiration occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells , with most reactions taking place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and in the mitochondria of eukaryotes. cellular respiration 4 steps i. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process, while the other two pathways are aerobic. Where do each part of cellular respiration occur? Review the steps of the krebs cycle:

Glycolysis is an anaerobic process, while the other two pathways are aerobic.
This step also produces more atp. 4 steps of aerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen in order to generate energy (atp). Learn about cellular respiration and how the electron transport chain uses the products of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle to complete the final steps in the process and convert food into energy. in performing cellular respiration, it'll probably be more on the order of 29 to 30 atps. cellular respiration occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells , with most reactions taking place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and in the mitochondria of eukaryotes. The steps of cellular respiration in order cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (atp), and then release waste products. Without cellular respiration gerald would be dead. The respiratory machinery is located in the cells of the body. This chapter will teach you the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration and take you. The krebs cycle uses pyruvic acid to create atp, along with additional molecules like nadh, fadh2, and co2. In the second stage, the pyruvic acid undergoes incomplte oxidation i.e., fermentation. In essence, the energy that was in covalent bonds of the glucose molecule is being released.
14+ Steps Of Cellular Respiration In Order Images. Two phosphate groups are attached to one molecule of glucose, atp converted to adp. Phases of complete glucose breakdown. What is the primary energy molecule. cellular respiration occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells , with most reactions taking place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and in the mitochondria of eukaryotes. cellular respiration is a catabolic process, resulting in the oxidation of organic molecules to release energy.
Glycolysis (cellular respiration 1 st stage) "the breakdown of glucose up to the formation of pyruvic acid is called glycolysis" steps of cellular respiration. The four steps of cellular respiration are glycolysis, acetyl coa formation, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.