malignant otitis externa is a severe form of an otherwise benign infection that is occasionally encountered in elderly diabetic patients.
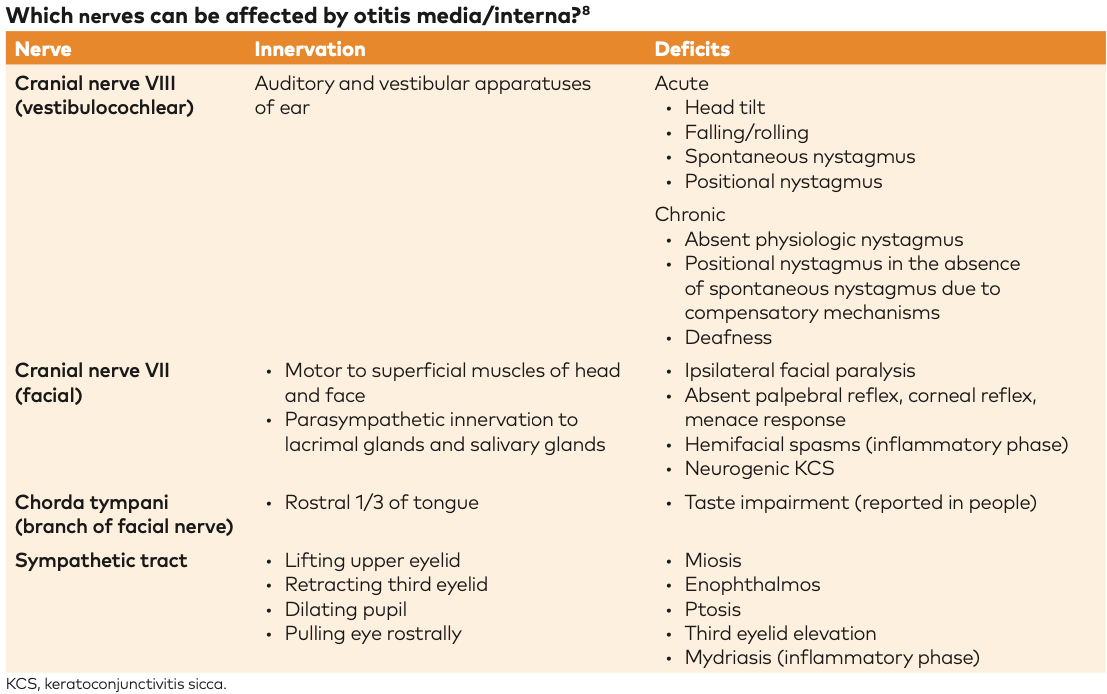
Otalgia often out of proportion for routine otitis externa. malignant otitis externa is otitis externa which has spread to cause osteomyelitis of the skull base. otitis externa is an inflammatory condition of the external auditory canal (the ear canal). Cn ix, x, or xi involvement. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most isolated microorganism and it affects mostly to diabetic, elderly, and immunocompromised individuals.

External otitis is often caused by bacteria that are hard to treat, such as pseudomonas.
External otitis is often caused by bacteria that are hard to treat, such as pseudomonas. 155 other ear, nose, mouth and throat diagnoses with cc; malignant otitis externa is caused by the spread of an outer ear infection (otitis externa) also called swimmer's ear. Cn ix, x, or xi involvement. Necrotizing / malignant otitis externa. malignant otitis externa is otitis externa which has spread to cause osteomyelitis of the skull base. malignant otitis externa is a disorder that involves infection and damage of the bones of the ear canal and at the base of the skull. Due to the high incidence of morbidity and mortality of the. malignant otitis externa requires urgent diagnosis and treatment. otitis externa (ear canal infection), malignant; In 1959 meltzer and kelemen identified a case of osteomyelitis of the temporal bone due to pseudomonas and malignant otitis externa was otitis externa (also known as external otitis or swimmer's ear) is an infection of the external auditory canal that is most often caused by acute bacterial infection and is frequently associated with hot, humid weather and water exposure. National guidelines state that a diagnosis of aoe requires the.
It was first reported in the literature by toulmouche in 1838. malignant otitis externa is caused by the spread of an outer ear infection (otitis externa), also called swimmer's ear. External otitis is often caused by bacteria that are hard to treat, such as pseudomonas. Signs and symptoms of malignant. Superior extensive inflammatory phlegmon along the temporalis and temporal subgaleal region.
Granulation tissue often seen in the ear canal floor.
Infection extends into ear canal cartilage. Effective tool for the diagnosis, but of limited value in predicting outcome. malignant otitis externa is a disorder that involves infection and damage of the bones of the ear canal and at the base of the skull. Pulcinic, mahdyounp, cuae, gahidei, castillo l, guevara n. Damage to the cranial nerves, skull, or brain return of infection, even after treatment It is due to pseudomonas aeruginosa and anaerobes causing a mound of tissue in the external canal Describe the advantages and disadvantages. Causes malignant otitis externa is caused by the spread of an outer ear infection (otitis externa) also called swimmer's ear. No appreciable collection at present. Pathogenesis, clinical features, and diagnosis. Necrotizing / malignant otitis externa. Acute otitis externa, colloquially known as "swimmer's ear", is an acute inflammation of the external auditory canal with a typically infectious etiology. 154 other ear, nose, mouth and throat diagnoses with mcc;
malignant otitis externa (moe) is an invasive infection of the temporal bone that is classically caused by pseudomonas aeruginosa. The condition can damage cranial nerves, bone tissue, and in extreme cases even result in death. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is most common causative organism (accounts for 95% of cases) staphylococcus aureus accounts for the remaining cases. This page includes the following topics and synonyms: No appreciable collection at present.

Acute otitis externa, colloquially known as "swimmer's ear", is an acute inflammation of the external auditory canal with a typically infectious etiology.
Medical knowledge of malignant otitis externa is primarily derived from retrospective case series. In 1959 meltzer and kelemen identified a case of osteomyelitis of the temporal bone due to pseudomonas and malignant otitis externa was Evidence of left mastoiditis with no intracranial extension. malignant otitis externa is necrotising external otitis. malignant otitis externa is more common in people who have diabetes or a compromised immune system, but it can also occur in people who do not have these conditions. malignant otitis externa (moe) is an uncommon condition mainly found in the elderly or in diabetics (phillips and jones 2013). Increasingly, however, nonpseudomonal cases are being reported. malignant otitis externa, or necrotizing otitis externa, is a rare disease associated with osteomyelitis of the skull base, which may result in cranial nerve deficit, abscess, and death. malignant (necrotizing) external otitis (also termed malignant otitis externa) is an invasive infection of the external auditory canal and skull base, which typically occurs in elderly patients with diabetes …. Effective tool for the diagnosis, but of limited value in predicting outcome. malignant or necrotizing otitis externa is a form of otitis externa that is more common in older patients with uncontrolled diabetes or in patients with immunodeficiency. This page includes the following topics and synonyms: Usefulness of ct scans in malignant external otitis:
47+ Malignant Otitis Externa Prognosis Background. Describe the advantages and disadvantages. Damage to the cranial nerves, skull, or brain return of infection, even after treatment Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most isolated microorganism and it affects mostly to diabetic, elderly, and immunocompromised individuals. 154 other ear, nose, mouth and throat diagnoses with mcc; malignant otitis externa (moe) is an aggressive skull base osteomyelitis, typically starting laterally from the external auditory canal;
Usefulness of ct scans in malignant external otitis: malignant otitis externa. Untreated, the infection can spread to nearby tissue and bone.