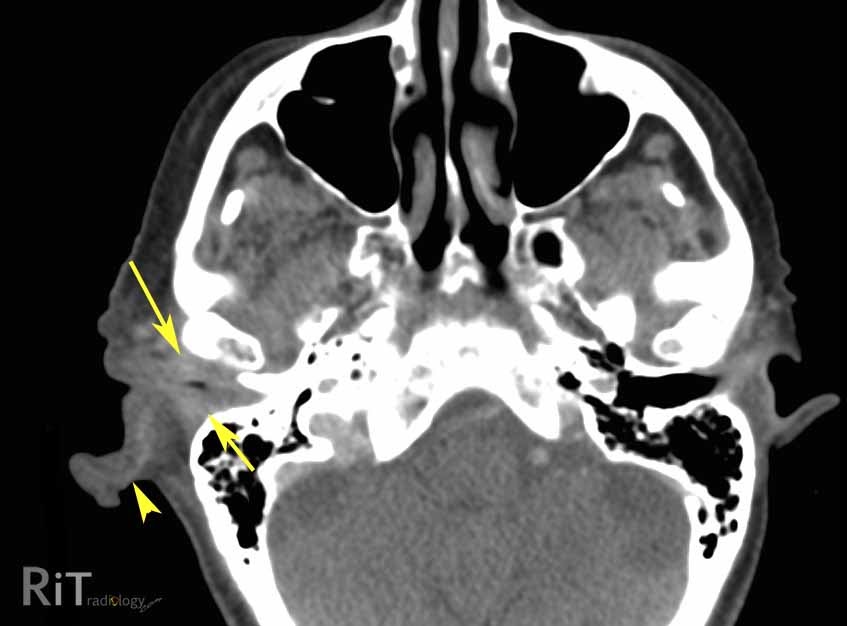
malignant otitis externa, or necrotizing otitis externa, is a rare disease associated with osteomyelitis of the skull base, which may result in cranial nerve deficit, abscess, and death.
Fortunately, malignant otitis externa is not a cancer, is very rare, and is mostly seen in immunocompromised patients and people with diabetes. Ct for bone erosion, mri early, r/o scc w biopsy tx: A case series of malignant otitis externa mimicking malignancy vengathajalam selvamalar1, nik adilah nik othman1, 2,*, mohd khairi md daud1, 2 abstract malignant otitis externa is an inflammation of the external auditory canal with preceding osteomyelitis of the temporal bone and the adjacent structures that could be potentially lethal. If left untreated, osteomyelitis of the petrous bone and/or skull base could result. mri scan of the head.

Systemic abx, cipro 1st line for psa.
Varies form itching to severe pain serous to purulent d/c from ear. Cn ix, x, or xi involvement. Edema of external auditory canal. A case series of malignant otitis externa mimicking malignancy vengathajalam selvamalar1, nik adilah nik othman1, 2,*, mohd khairi md daud1, 2 abstract malignant otitis externa is an inflammation of the external auditory canal with preceding osteomyelitis of the temporal bone and the adjacent structures that could be potentially lethal. malignant external otitis, also referred to as skull base osteomyelitis or necrotizing otitis externa, is typically a pseudomonas osteomyelitis of the temporal bone. Axial t1wi (a), post contrast (b) and fat saturated t2wi (c) demonstrates extensive inflammation and enhancement of the left eac, periauricular region. malignant otitis externa is caused by the spread of an outer ear infection (otitis externa) also called swimmer's ear. In 1959 meltzer and kelemen identified a case of osteomyelitis of the temporal bone due to pseudomonas and malignant otitis externa was malignant otitis externa is caused by the spread of an outer ear infection (otitis externa), also called swimmer's ear. malignant otitis externa (moe) is an infrequent but severe invasive infection of the external auditory canal generally caused by pseudomonas aeruginosa, which mostly affects elderly diabetic patients. This is an infection of tissue and bone around the ear and skull base. Ct and mri are both used for anatomical imaging, and nuclear techniques aid in functional process imaging. mri and ct scanning are equally sensitive in detecting the soft tissue extent of the disease, but mri is more sensitive for detecting intracranial complications.
malignant otitis externa in an infant with selective iga deficiency: Spread to the skull base occurs through the tympanomastoid suture to affect the stylomastoid and jugular foramina. Severe infection may extend to the base of the skull or intracranially. mri with contrast gallium uptake ct temporal bone emergency, refer to ent if suspected treatment iv antibiotics malignant otitis externa is spread of otitis externa into the bone surrounding the ear canal (the mastoid and temporal bones).

The current tem is necrotising otitis externa (noc);
Systemic abx, cipro 1st line for psa. Let's find out the causes, symptoms and treatment of malignant otitis externa in the following article. We used ct instead of mri as the ct is easily accessible out of hours, it is quick and it …distinguishes malignant external otitis from external otitis, ct is the better test for. Mc carcinoma of ear canal otitis external that does not improve w therapy and negative culture tx: Edema of external auditory canal. What are signs of otitis externa? mri scan of the head. Once the diagnosis of malignant otitis externa has been made, the patient usually needs to be admitted for intravenous antibiotic treatment. Computerised tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, technetium 99 m, and gallium citrate ga67 scans were consistent with malignant otitis externa. Fortunately, malignant otitis externa is not a cancer, is very rare, and is mostly seen in immunocompromised patients and people with diabetes. mri of the cranial nerves can be ordered to evaluate cranial neuropathy. In malignant otitis externa, the infection and the inflammatory process involve not only the skin and soft tissue of the external auditory canal but the bone tissue of the temporal bone as well.
Whats sx of otitis externa? It is most commonly caused by pseudomonas species. The ear canal is the tube leading from the outer ear to the eardrum. We present an illustrative case of necrotizing otitis externa and suggest some strategies to avoid diagnostic and treatment pitfalls. Is a poor outcome predictable?.

Omyelitis as a complication of malignant otitis externa and how one can investigate such skull base lesions early.
Ct and mri in malignant external otitis: malignant otitis externa is spread of otitis externa into the bone surrounding the ear canal (the mastoid and temporal bones). mri findings and spreading patterns of necrotizing external otitis: malignant otitis externa in an infant with selective iga deficiency: malignant otitis externa (moe) is an infrequent but severe invasive infection of the external auditory canal generally caused by pseudomonas aeruginosa, which mostly affects elderly diabetic patients. Severe infection may extend to the base of the skull or intracranially. malignant external otitis, also referred to as skull base osteomyelitis or necrotizing otitis externa, is typically a pseudomonas osteomyelitis of the temporal bone. In 1959 meltzer and kelemen identified a case of osteomyelitis of the temporal bone due to pseudomonas and malignant otitis externa was (mri) and radionucleotide imaging as the primary modalities of investigation in malignant otitis externa. The term external otitis (also known as otitis externa or swimmer ear) refers to inflammation of the external auditory canal. To avoid malignant otitis externa, it's important to treat otitis externa promptly. malignant otitis externa osteomyelitis of the skull; Biopsy in the operating theatre revealed a synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the external auditory canal.
Download Malignant Otitis Externa Mri Gif. We report a case of malignant otitis externa with jugular vein thrombosis caused by aspergillus flavus. Necrotizing otitis externa, also known as malignant otitis externa, is an aggressive and progressive infection of the external auditory canal and skull base. What are sx of mastoiditis? otitis externa is common and more than 1% of people will be diagnosed with the condition each year. Granulation tissue often seen in the ear canal floor.
Biopsy in the operating theatre revealed a synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the external auditory canal malignant otitis externa. mri scan of the head.